Ginger (Zingiber officinale) production is another agricultural goldmine.
First, we would like you to consider an improved method of ginger production. Ginger-under-no-till. This is a sustainable method of ginger production that reduces costs, increases yields, and protects our environment.
Read also: 11 amazing health benefits of Ginger
There are 4 main stages in ginger production, i.e., planning, pre-planting, planting and agronomic practices, harvesting, and packaging.
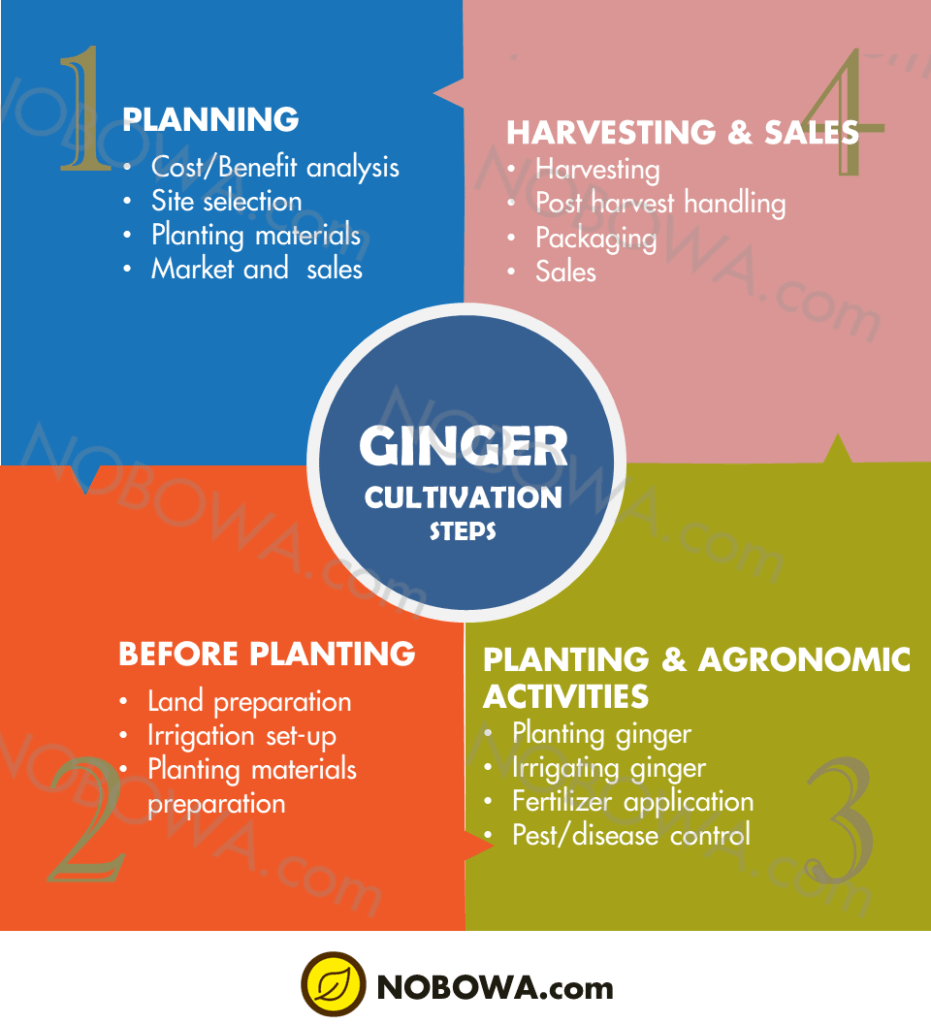
Stage 1: Planning
Do not skip this stage.
This is the stage where you visualize all the processes to the end, from the start. During planning, you put down all the key components and requirements of ginger production and consider strategies you will use to get the best possible outcome.
At this stage you try to answer key questions like;
What are the cost and benefits of producing ginger?
Do a comprehensive cost/benefits analysis on ginger production. Do a detailed budget that lists all the needed materials and labour to cultivate a specified area. Cost your own labour and inputs you may not buy.
Compare costs of various technologies. Make your choice based on applicability, affordability and sustainability.
What is the recommended site for ginger production?
Land with well-drained loamy soils is best for ginger. Avoid waterlogged areas. The site must be accessible for easy carting of harvest and other mechanical activities.
Consider carrying out a soil test. The results will help you know the fertility of the land and the available soil nutrients. This will help you decide the amount of fertilizer or manure to apply.
Where and how to market and sell ginger?
Options include; selling fresh at the open foodstuff market; selling fresh and in bulk to alcoholic beverage producers, fresh to aggregators; processing into powder or juice.
Have a clear idea of this and even make some contact with buyers before you start.
Where and how to get quality planting materials?
Know where to get your quality ginger planting materials for planting. Approximately 37.5bags (1,500kg) of ginger materials is required per hectare.
| Local variety | Exotic variety | |
|---|---|---|
| Suitable varieties | White type and Yellow type | Yellow Jamaican, Sierra Leonean selection, Peruvian |
| Source of planting materials | Nobowa or Established farms in growing areas. | Input dealers; Horticulture Department, KNUST, Kumasi. |
Stage 2: Pre-planting
Land preparation
Different land preparation methods come with varying costs. There is the conventional method which involves slashing or clearing weeds, burning or removal of the residue and ploughing the soil. Then there is the no-til method where the cleared residue is left to cover the surface of the land and you do not plough.
Read more about conventional versus conservation methods.
Irrigation
- Rainfall
Ginger growing areas enjoy two rainy seasons. Ginger matures between 6 – 8monts after planting. Therefore, you need adequate rainfalls in both seasons to obtain optimum yields for ginger.
- Irrigation
Providing irrigation is an advantage. You can be sure of higher yields whenever you plant. Sprinkler irrigation is best for ginger.
Planting material preparation
Ginger is grown from the same root/rhizome that is consumed. The whole is cut into smaller sizes with a sharp knife and treated before planting. The size of cuttings depends on humidity and soils moisture content.
Stage 3: Planting and agronomic practices
Planting ginger
You can plant ginger after consistent rainfalls between March and May. This pattern is changing due to climate change. The use of sustainable technologies will ensure production in adverse weather. To ensure maximum sprouting of ginger after planting, mulch and/or irrigate.
- Planting distance
No ridges – 20cm apart
Ridges – 20cm x 30cm
- Planting depth
4 – 10cm deep.
- Considerations for the right distance and depth;
How your land is prepared
The size of the planting material will determine the depth of planting.
The pertaining weather conditions
Irrigating ginger
The sprinkler irrigation system is best suited for ginger. Explore other systems and test if suitable. Where rainfall is not well distributed, irrigate lightly but evenly every 4-7 days depending on the type of soil. Avoid waterlogging.
READ ALSO: TYPES OF IRRIGATION: ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Fertilizer application
Use the soil test report as a guide for fertilizer application. Apply 25-30 tons/ha of well-decomposed organic manure during land preparation. Or apply a total of 600 kg/ha (12 bags) of NPK 15-15-15 in 2 split applications, 5 bags at 3 weeks after sprouting and 7 bags at 3 months after planting.
Controlling weeds in ginger
Effectively control weeds by handpicking during the growing season or practising shallow weeding to avoid damaging plants.
READ ALSO: INORGANIC FERTILIZER: ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Pests control in ginger
Although there are no serious pests due to the pungent nature of the crop, cutworms, aphids, root-knot nematodes, stem borers, African black beetles and rodents sometimes attack the shoots or roots. Practice IPM or apply EPA approved chemicals.
Disease control in ginger
Diseases like bacterial wilt, leaf spot, fusarium and pythium rot, soft rot and cork rot can attack the plants. However, you can effectively control them by practising strict hygiene, use of bio-agents like (Trichoderma), improving drainage and ensuring proper sett dressing with EPA approved fungicides before planting.
Read also: MANAGING CROP PESTS WITH INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT (IPM)
Stage 4: Harvesting and Packaging of ginger
Harvesting ginger
Ginger is ready for harvesting 5-10 months after planting. The tops start dying and dislodging. Harvest the rhizomes by hoeing the field or beds. Or by toppling the ridges. However, take care not to bruise or injure the rhizomes during harvesting. Also, harvest ginger for the fresh export market earlier (about 7 months). At that stage, the fibre content of the rhizome is low.
Yield of ginger
The yield before drying is about 15-20 tons/ha. That is about 300-500 bags.
Post-harvest handling of ginger
After digging, shake off the soil, remove all roots and wash rhizomes thoroughly. Dry for 2 days in the shade.
Drying ginger after harvest
Dry uniformly to get quality ginger. It may be scraped or non-scraped depending on the market requirement. Also, dried ginger’s value depends on its whiteness achieved by thorough washing and uniform drying. Liming (2% solution for 6 hrs followed by sun-drying for 10 days) improves colour, appearance. Also, it protects the rhizomes from mildew and other pests. Dry to 8-10% moisture content, store at 10-120 c and 90% relative humidity.
Grading ginger after harvest
According to size and colour. The best grade consists of large hands and fingers and is free of dirt and traces of mildew.
Market specification
Ginger should be clean and uniform in colour. For fresh ginger, the fibre content should be 3.5% or below (export); or with higher pungency (local).
Packaging of ginger
Dried ginger can be packed in 25 and 50 kg meshed bags. You can package fresh ginger for export in (288x203x108)mm or (457x297x153)mm box.


