Plants use water to survive and grow. Water helps plants to transport nutrients and give energy. It is one of the most important, if not the most important, compound or substance in plants. Water makes up to about 95% of the body of most plants.
Plants use water in four ways to survive and grow.
Read also: Types of Irrigation: Advantages and Disadvantages
Plant’s structure
Animals have an internal or external skeleton that gives them their structure and protects their organs. In most plants, to grow and support such rigidity, they need water. Some trees get this rigidity from lignin, a polymer that binds fibrous materials together.
The plant cell has a part called the vacuole, which is the largest part of the cell. Water fills the vacuoles and they make sure the cell maintains its shape. According to regenerative.com – If the plant receives enough water, each vacuole in each cell keeps the cell walls at the right tension. In combination, all the cells give the plant its strength. This water pressure within the cells is called ‘turgor’ and because the strength is derived from a liquid source, the strength retains the flexibility that animal skeletons lack. This allows the plants to adapt to surroundings and bend in the wind. Also to move towards the sun as it traverses the sky during the day to get the most energy for photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
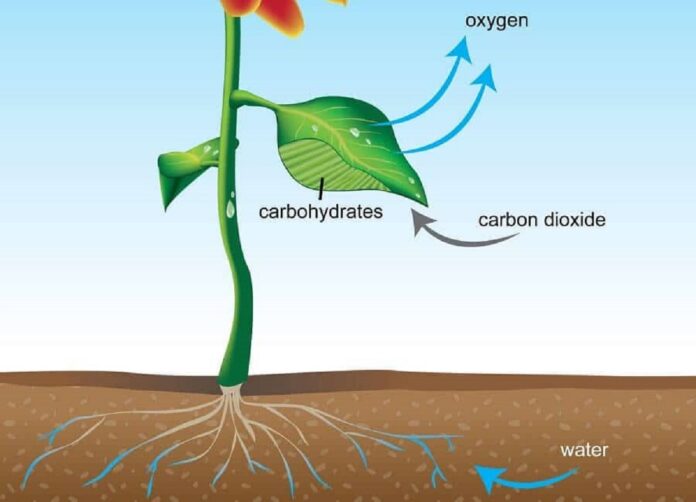
Plants produce energy for growth and survival by the process of photosynthesis. By definition; Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy (from the sun) into chemical energy (in the form of sugars). The energy can later be released to fuel the organisms’ activities – (Wikipedia).
Water is a part of this process. According to regenerative.com – For the molecules of sugar to form they need carbon dioxide (which they absorb from the air) and hydrogen. The hydrogen comes from the water in the plant and comes up through the plant from the roots to the leaves. Whiles plants release oxygen as a by-product of the photosynthesis process, they also need a small amount of it in solution to help ease the function. Water provides this as well.
Translocation
Translocation is the movement of water through plants. By the process of translocation, nutrients move around in the plant and to parts that need the nutrients. Do you know why water in the soil is very important for the plant’s growth?
Plants absorb nutrients in solution. Therefore, adequate water in the soil helps plants in nutrient absorption. Soil nutrients move up through the roots of the plant in a water solution by capillary action. The process of capillary action moves the nutrients in solution to the various parts of the plants including the leaves for photosynthesis.
It also helps to carry the products of photosynthesis mainly sugars, down the plants to the roots and other parts to enable them to grow.
Transpiration
It is essentially evaporation of water from plant leaves. From water.usgs.gov: Transpiration is the process by which moisture moves through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves. Here it changes to vapour and is released into the atmosphere.
This is the explanation from regenerative.com.
Transpiration occurs when stomata, a kind of pore, open on the leaf to allow for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with the atmosphere during photosynthesis. Indeed, some of the oxygen that the plant releases is contained in the water vapour that is transpired. Not only does the transpiration effectively give the space into which the essential carbon dioxide can flow. It also prompts the plant to take up more water from the soil (bringing with it nutrients), so helping to keep the internal system of the plant in balance. Transpiration also keeps the plant cool – think of transpiration as being a bit like sweating in humans!
It further explains that;
Besides the individual rates that different species have, rates of transpiration will vary depending on a number of factors. These include temperature (warmer temperatures causes more transpiration), light (plants transpire less in the dark) and humidity (it is easier for a plant to release moisture into drier than saturated air.
Wind will also cause more transpiration to occur, partly as still air tends to become more humid, and the wind moves this air away from the leaves.
Also, the amount of moisture in the soil that is available for uptake by the plant, affects transpiration, like photosynthesis and translocation. If there is insufficient water in the soil, transpiration slows, as do the other process. Furthermore, the plant will begin to show signs of distress, such as curling and browning of leaves.
In conclusion
These four processes are very important to plant and they all need water. Water requirement levels may differ from species and conditions. Water needs to be sufficiently available in the soil for plants to carry out these natural processes without any hindrance. Enough water translates into a healthy plant.