Did you know that what you may call waste in your house is of great value? Compost is one valuable product that can come from the simple selection and treatment of this household waste. Learn to make good use of household waste through composting.
What is compost?
It is a mixture of decaying organic substances such as dead leaves or manure, used as a fertilizer. In other words, compost is an organic matter that has been decomposed and recycled as a fertilizer and soil amendment. Compost is a key ingredient in organic farming.
What is composting?
Composting is a simple and easy way to reduce household waste. It is useful for recycling kitchen wastes, weeds, leftovers and crop residues.
Read also: Why is Organic Fertilizer better?
The types of compost
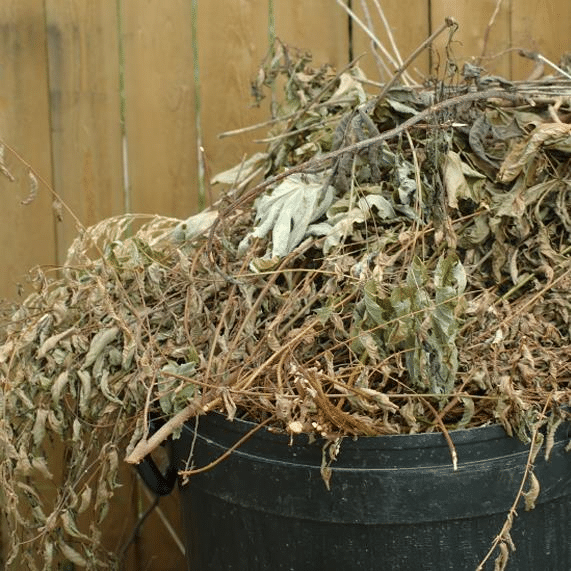
Yard trimmings
They are small branches, limbs, and leaves that are composted and used as a fertilizer. Since 1989, the City of Austin, Texas has been using this method to produce fertilizer or compost called Dillo Dirt. Dillo Dirt contains treated municipal sewage along with yard trimmings.
Food waste
Compostable food scraps are one of the best and most readily available sources of organic materials for domestic composting. Food scraps like vegetables and fruit waste, stale bread, grains, meal leftovers, etc.
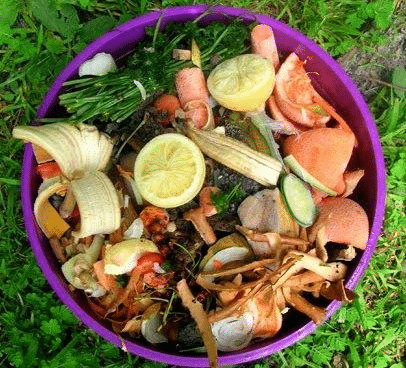
Leaves compost
It is a kind of compost whereby the leaves of trees are used in the preparation. The leaves make a dark, rich, earthy organic matter that can be used as soil. It adds nutrients to the soil, and the larger particle size helps enhance the tilth and loosen compacted earth.

Manure compost
Manure compost is organic matter used as organic fertilizer which improves soil fertility. Compost manure is mostly derived from animal faeces (cattle, poultry, etc).

Read also: Earthworm Benefits to Soil Fertility and Plants in Agriculture
Mushroom compost
It is a slow-release organic plant fertilizer. The compost is made by mushroom growers using organic materials such as hay, straw, poultry or cattle manure, hull and corn cobs.

Vermicompost
Vermicompost involves the use of various species of worms, usually red wigglers, white worms and other earthworms to convert organic waste into fertilizer. Vermicast, also a fertilizer, is the end the end-product of the breakdown of organic matter by the worms.

Read also: Vermiculture and Vermicomposting: Benefits and Constraints In Organic Farming
Types of materials you can use to compost
You may use a combination of these materials in your compost. Remember, good compost requires a good proportion of different materials. The list is not exhaustive, and you can experiment with other materials.
- Leaves
- Food scraps such as bread, vegetables, cereal, peelings, etc.
- Pet bedding from herbivores only (rabbits, etc).
- Old herbs and spices.
- Manure (organic).
- Old wine.
- Dust from sweeping and vacuuming.
The Importance of Compost
- Compost improves soil structure and porosity. Porosity is several pores or open spaces between the soil particles. The movements of worms, insects and roots create the pores.
- It builds organic matter in the soil.
- Compost reduces the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
- It helps improve all soil types, especially sandy and clayey soil. Sandy soil has very little water and nutrient retention. Sandy soil compost, therefore, helps to bind the particles together and increases the soil’s ability to retain moisture and nutrients.
- It enriches the soil by helping retain moisture and suppress plant diseases and pests.
- Compost encourages the production of beneficial bacteria and fungi that break down organic matter to create humus (a rich nutrient-filled material).
Read also: Inorganic Fertilizer: Advantages and Disadvantages
What you need to start composting
To get started, you need the right tools and correct ingredients. The tools include;
- A standard plastic compost bin or a homemade compost bin (made from timber).
- A compost turner and garden fork.
Consider the following groups of ingredients for composting.
- Green organic ingredients: Kitchen fruits and vegetable scraps, eggshells, flowers, manure (cow, chicken or sheep), a small amount of carbohydrate (rice and pasta), green cut grass and clippings, tea bags etc.
- Brown ingredients: Newspaper, soil, dried leaves, straw, twigs, shredded cardboard.
How to prepare compost
Once you have the ingredients, preparing compost is simply a matter of adding them into the bin in the right quantities. You need to use both green and brown ingredients to have good compost.
Step One
The first step is to find the right location for the compost bin. Position the bin in such a way that you can have access to it from your kitchen. You can place the compost in the sun or the shade but the warmer the location, the faster the compost will work.
Step Two
Place the brown ingredients (dried leaves, newspaper etc) at the bottom of the compost bin and water thoroughly. The water promotes bacterial growth which allows the compost to start breaking down.
Step Three
This step involves the addition of the green ingredient (kitchen fruits and vegetable scraps etc) and it should be roughly the same thickness as the first brown layer.
Step Four
This step involves the repetition of steps two and three. That is the addition of green and brown ingredients at the same thickness and some water to moisten.
Step Five
In this step, one can choose to add a thin layer of soil from the garden to seed the compost. The seed is about kick-starting the compost by introducing ingredients rich in useful microorganisms.
Step Six
You can add food scraps and other green materials to the bin. Be sure to cover the kitchen scrap bucket with a layer of brown material to build balanced and productive compost. The compost is ready when it looks like rich, dark soil. Tilt the bin and scrape away the finished compost at the bottom, or lift the bin and start a new pile.
Do not compost…
- Plastics.
- Weeds.
- Chemicals
- Diseased Plants.
- Metals.
- Glossy Magazines.
- Treated Pine Sawdust.
- Gum leaves.
Now that you know about composting, try it at home and let us know how it goes.
Reference:


